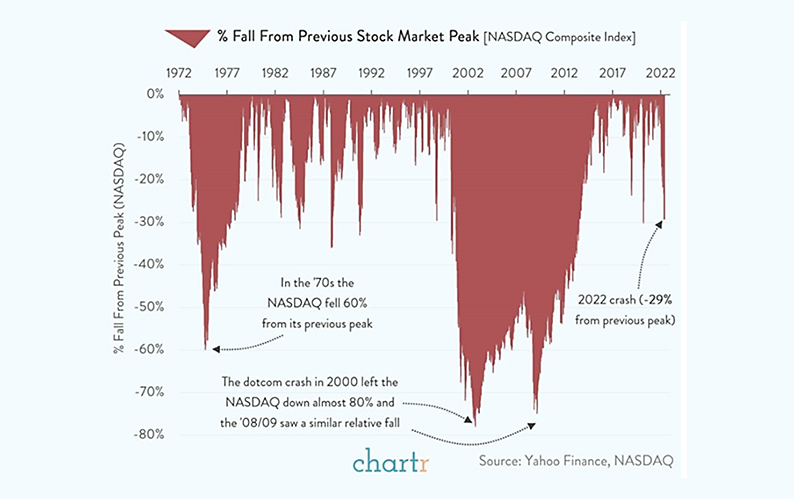
The second quarter of 2022 proved to be a challenging period for some of the world’s largest technology companies as central banks globally ramped up interest rates to combat the looming threat of inflation. Amidst these changing economic conditions, investors began to reevaluate their positions in tech stocks, leading to significant declines in valuations across the sector.
The First Quarter: A Prelude to Challenges
The challenges for major technology companies began in the first quarter of the year. Russia’s invasion of Ukraine had far-reaching consequences that extended well beyond geopolitical boundaries. The invasion disrupted supply chains and added to the challenges already posed by the lingering impacts of the COVID-19 pandemic.
For investors, this meant that technology companies, despite their resilience during the pandemic, were not immune to global events. While tech stocks had been the darlings of the stock market in recent years, the situation began to change as the first quarter unfolded.
The Market Responds
The impact of these challenges quickly manifested in stock prices. The S&P 500, a broad index representing the performance of 500 of the largest companies in the U.S., experienced a decline of approximately 5% during the first quarter. However, it was the technology-heavy Nasdaq Composite index that bore the brunt of the market’s concerns, posting a decline of 22% during the same period.
The Second Quarter: A Deteriorating Situation
As the second quarter began, technology companies found themselves grappling with increasingly complex challenges. The Federal Reserve, the central bank of the United States, shifted its focus towards addressing the rising threat of inflation. To counter inflationary pressures, the Federal Reserve adopted a more hawkish stance, signaling its intent to raise interest rates.
This change in monetary policy had a profound impact on technology companies. Rising interest rates meant that borrowing costs would increase, potentially affecting profitability. Additionally, higher interest rates could lead to a rotation of funds out of growth-oriented technology stocks into other sectors, where companies might be better positioned to weather the economic headwinds.
Tesla’s Troubles
One prominent example of a technology company grappling with these challenges was Tesla, the electric vehicle (EV) manufacturer. Tesla had been a darling of the stock market for years, with its charismatic CEO, Elon Musk, at the helm. However, the second quarter of 2022 proved to be a significant test for the company.
During the quarter, Tesla experienced its largest quarterly drop since its initial public offering (IPO) in 2010. The stock price of the electric vehicle maker sank nearly 38% during this period. It was a turbulent quarter for Tesla, marked not only by stock price declines but also by a high-profile bid from CEO Elon Musk to acquire the social media giant Twitter for a staggering $44 billion.
Musk’s ambitions extended beyond the realm of electric vehicles, hinting at a broader vision that encompassed the digital landscape. However, Tesla’s stock price reflected the concerns of investors who were already navigating a challenging market environment.
Amazon Faces Headwinds
Another tech giant that faced significant headwinds during the second quarter was Amazon. The e-commerce behemoth saw its stock price drop by almost 35%, marking its most substantial decline since the third quarter of 2001. The challenges for Amazon were multifaceted.
In April, Amazon reported first-quarter earnings that fell short of analysts’ estimates. Slowing revenue growth contributed to concerns about the company’s future prospects. Additionally, in early June, Amazon announced the resignation of Dave Clark, the CEO of its global consumer business. Clark’s departure was notable as he was set to take on the role of CEO at Flexport, a supply chain software startup, in September.
These developments raised questions about Amazon’s ability to maintain its growth trajectory and adapt to the evolving landscape of e-commerce and logistics.
Alphabet and Microsoft Grapple with Declines
Alphabet, the parent company of Google, also faced challenges during the second quarter. The company’s shares ended the quarter down by nearly 22%, marking its poorest performance since the fourth quarter of 2008. Google’s advertising-centric business model was susceptible to economic headwinds, and investors appeared to be reevaluating their expectations.
Microsoft, another tech stalwart, witnessed its shares drop by approximately 17% during the second quarter. This decline was the sharpest since the second quarter of 2010. While Microsoft had enjoyed steady growth in recent years, the changing economic landscape prompted investors to reassess their positions.
Apple’s Rocky Quarter
Apple, one of the world’s most valuable companies, faced a challenging second quarter. The tech giant’s stock fell by almost 22%, marking its worst performance since the fourth quarter of 2018. During that period, Apple reported lower-than-expected guidance, and the broader stock market experienced a steep selloff.
Apple’s fortunes are closely tied to its product launches and the demand for its flagship iPhone. Any signs of weakness in these areas can send ripples through the entire technology sector, impacting investor sentiment.
Meta Platforms: A Shift in Identity
Meta Platforms, formerly known as Facebook, witnessed its stock decline by more than 27% during the second quarter. This was a comparatively better outcome than the first quarter when the stock’s value compressed by about 34%.
In February, the social-network operator reported a decline in its count of daily active users on Facebook for the first time. This development raised concerns about the company’s ability to sustain its user base and growth trajectory. The company’s shift towards embracing the metaverse—a virtual, digital realm—represented a strategic pivot, but it also introduced uncertainties.
Meta Platforms’ decision to change its ticker symbol from FB to META reflected its new corporate identity, emphasizing a stronger focus on digital worlds where people can transact and interact. This rebranding effort aimed to position the company for a future where the boundaries between the physical and digital worlds blur.
Outperformers Amidst the Turbulence
While major technology companies grappled with declining valuations and economic uncertainties, several other companies managed to outperform expectations during the second quarter. Drugmakers Eli Lilly and Merck, cereal company Kellogg, and discount retailer Dollar General were among the notable performers, posting gains of at least 10% during the quarter.
These companies demonstrated resilience in the face of economic challenges, offering investors opportunities for growth and stability amidst a volatile market.
Navigating a Changing Landscape
The changing economic landscape, marked by rising interest rates and geopolitical uncertainties, has presented technology companies with unique challenges. Investors, in turn, have been forced to reevaluate their positions and assess the long-term prospects of these industry leaders.
One key consideration for investors has been the potential impact of rising interest rates on the borrowing costs of technology companies. Historically, low interest rates have facilitated access to cheap capital, enabling tech companies to fund research, development, and expansion. However, as interest rates rise, the cost of borrowing increases, potentially affecting profitability and capital allocation strategies.
Another factor in play is the rotation of funds. Rising interest rates can prompt investors to seek alternative investments that offer more attractive risk-adjusted returns. This shift in capital allocation can lead to a reduction in demand for growth-oriented technology stocks.
The Broader Economic Landscape
The challenges faced by major technology companies are not isolated incidents but rather reflections of broader economic trends. Rising interest rates are a response to concerns about inflation—a phenomenon characterized by the increasing prices of goods and services over time.
Central banks, including the Federal Reserve, have a mandate to maintain price stability and employment. Inflation erodes the purchasing power of currency, making goods and services more expensive. To combat this erosion of value, central banks often raise interest rates to cool down economic activity and prevent prices from spiraling out of control.
However, higher interest rates can have ripple effects throughout the economy. Borrowing costs rise for businesses and consumers, potentially reducing spending and investment. Additionally, higher interest rates can impact the valuations of financial assets, including stocks.
The Role of Investor Sentiment
Investor sentiment plays a crucial role in shaping the performance of technology stocks. Sentiment can be influenced by a wide range of factors, from macroeconomic trends to company-specific developments. When sentiment is positive, investors are more likely to buy and hold stocks, contributing to rising valuations. Conversely, when sentiment turns negative, investors may sell, leading to declining stock prices.
In the case of technology companies, sentiment can be particularly sensitive to shifts in the economic landscape. These companies are often viewed as growth stocks, with valuations based on expectations of future revenue and earnings growth. When economic conditions become less favorable for growth, as signaled by rising interest rates and inflation concerns, sentiment can quickly sour.
Looking Ahead
As technology companies navigate the changing economic landscape, they face a series of strategic questions. How can they adapt to higher interest rates and inflationary pressures? What steps can they take to maintain growth and profitability in a shifting environment?
One potential avenue for technology companies is to focus on innovation and diversification. The tech sector has a long history of driving innovation and creating new markets. Companies that can continue to innovate and develop products and services that meet evolving consumer needs may find themselves better positioned for long-term success.
Additionally, diversification can help mitigate risks associated with economic fluctuations. By expanding into new markets or offering a broader range of products and services, technology companies can reduce their reliance on any single source of revenue.
Collaboration and partnerships may also play a crucial role in the tech sector’s response to changing economic conditions. By working together with other companies, including startups and established players in adjacent industries, tech giants can tap into new ideas, technologies, and markets.
The challenges faced by major technology companies during the second quarter of 2022 are a reflection of the dynamic and ever-changing nature of the global economy. Rising interest rates and concerns about inflation have created headwinds for the tech sector, prompting investors to reassess their positions.
While the short-term outlook may be uncertain, technology companies have a history of resilience and adaptability. By focusing on innovation, diversification, and collaboration, these companies may find ways to thrive in a changing economic landscape.
As investors continue to monitor economic developments and assess the risks and opportunities in the tech sector, one thing remains clear: the world of technology is bound to continue evolving, and the companies that can embrace change and stay ahead of the curve are the ones most likely to succeed in the long run.